Search results
Create the page "The Antarctic atmosphere" on this wiki! See also the search results found.
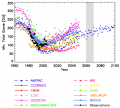
File:Figure 5.11 - Observations and model predictions of minimum September to October total column ozone.png ...r et al, 2005">Bodeker, G.E., Shiona, H. and Eskes, H. 2005. Indicators of Antarctic ozone depletion, ''Atmos. Chem. Phys.'', '''5''', 2603-2615.</ref>). Solid(543 × 488 (113 KB)) - 15:30, 6 August 2014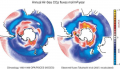
File:Figure 4.56 - Annual mean uptake of air-sea CO2 fluxes as calculated from OPA-PISCES 1990-1999.png ...ors), whereas south of 50°S, large regions act as a CO2 source for the atmosphere (red).(522 × 299 (218 KB)) - 15:30, 6 August 2014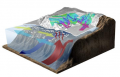
File:Figure 4.41 - Pictorial view of the ocean-ice system of the Ross Sea.png ...o the atmosphere (wavy vertical line) while the remainder circulated under the floating ice shelf causing basal melting. (illustration courtesy of Nationa(533 × 342 (194 KB)) - 15:31, 6 August 2014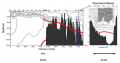
File:Figure 4.26 - Cross-section showing warm water penetrating the Pine Island Bay sub-ice shelf cavity.png ...tarc. Res. Ser.'', '''75''', 83-99.</ref>). The solid black area indicates the sea bed.(592 × 309 (119 KB)) - 15:31, 6 August 2014- ...page is part of the topic [[Antarctic climate and environment change over the next 100 years]]'' ...and and Antarctica). The amount of thermal expansion is non-uniform due to the influence of ocean currents and spatial variations in ocean warming. Global16 KB (2,491 words) - 13:16, 22 August 2014
- ...f the changes observed in recent decades. This is particularly the case in the ocean where we have few long time series of physical measurements and remar ...as near-surface air temperature it is possible to use the projections from the various models to derive various estimates of how temperature may change ov5 KB (788 words) - 16:49, 6 August 2014
- ...ciation, retreat of the ice sheet and its effects on global sea level, and the changing distribution of sea ice and its effect on climate are then describ ...tanding of the climate and biological changes that might be anticipated in the near future (Chapter 5).17 KB (2,554 words) - 16:45, 6 August 2014
- ...is page is part of the topic [[Antarctic climate and environment change in the instrumental period]]'' ...were reliant on sparse ship observations that were mainly collected during the summer months.22 KB (3,536 words) - 13:25, 22 August 2014
- ...page is part of the topic [[Antarctic climate and environment change over the next 100 years]]'' #[[Atmospheric circulation changes over the 21st century]]410 B (55 words) - 15:33, 6 August 2014
- :''This page is part of the topic [[Atmospheric change over the next 100 years]]'' ==Antarctic stratospheric ozone over the next 100 years==27 KB (4,305 words) - 16:22, 6 August 2014
- ...is page is part of the topic [[Antarctic climate and environment change in the instrumental period]]'' ==Antarctic stratospheric ozone in the instrumental period==43 KB (6,788 words) - 17:07, 22 August 2014
- ...is page is part of the topic [[Antarctic climate and environment change in the instrumental period]]'' ...random sample, and can ‘describe’ a significant proportion of the total circulation variability.54 KB (8,177 words) - 13:38, 22 August 2014
- :''This page is part of the topic [[Atmospheric change over the next 100 years]]'' ...he distribution of sea ice, and the seasonal to interannual variability of the Southern Hemisphere.29 KB (4,462 words) - 17:11, 22 August 2014
- :''This page is part of the topic [[The ice sheet in the instrumental period]]'' ...ange. The inescapable fact is that ice sheet behaviour manifests itself as the superposition of multiple responses on multiple time scales to multiple env13 KB (1,943 words) - 15:33, 6 August 2014
- ...is page is part of the topic [[Antarctic climate and environment change in the instrumental period]]'' ==General spatial and temporal characteristics of Antarctic snowfall==20 KB (3,125 words) - 15:33, 6 August 2014
- :''This page is part of the topic [[The Holocene]]'' ...ial to use proxy records to represent how Antarctic sea ice has changed in the past.24 KB (3,785 words) - 17:17, 22 August 2014
- ...page is part of the topic [[Antarctic climate and environment change over the next 100 years]]'' ...uperposition of the continuing gradual response to past climate change and the more rapid responses to present and future changes.26 KB (4,124 words) - 14:04, 22 August 2014
- :''This page is part of the topic [[The ice sheet in the instrumental period]]'' ...he ice sheet places different parts in markedly different positions within the global climate system and subjects them to different environmental drivers.3 KB (475 words) - 15:33, 6 August 2014
- ...rt of the topic [[Models of the physical and biological environment of the Antarctic]]'' ...reproduce reality. Such reality checks are often crude, given that most of the commonly used GCMs do not operate at a finer scale than one-degree squares.13 KB (2,051 words) - 15:33, 6 August 2014
- :''This page is part of the topic [[The last million years]]'' ...ng|thumb|'''3.9''' Main climatic events of the last 1 Million years in the Antarctic context]]35 KB (5,415 words) - 15:33, 6 August 2014
- :''This page is part of the topic [[The Holocene]]'' ...variability must be taken into account in understanding modern climate and the potential for future climate change.39 KB (5,945 words) - 15:33, 6 August 2014
- :''This page is part of the topic [[Marine biology in the instrumental period]]'' ...ated with the climate regime can be interpreted as major driving forces on the large scale biogeography of marine water breathing animals. These relations25 KB (3,817 words) - 15:33, 6 August 2014
- :''This page is part of the topic [[Observations, data accuracy and tools]]'' ...per, 2007">Smith, W. and Asper, V.A. 2007. New Ways to Collect Data in the Antarctic, EOS, Transactions American Geophysical Union, 88, no. 48, 525.</ref>).17 KB (2,672 words) - 15:50, 6 August 2014
- ...e gas concentrations increase at the present rate then temperatures across the continent will increase by several degrees and there will be about one thir ==The Geological Dimension (Deep Time)==48 KB (7,673 words) - 18:27, 22 August 2014
- ...CE Consortium. 2009. Review: Antarctic climate change and the environment, Antarctic Science, 1-23.</ref>). ...nline PDF version of the report is available to download without cost from the SCAR web site (http://www.scar.org/publications/occasionals/acce.html) or h142 KB (22,142 words) - 16:25, 6 August 2014
- :''This page is part of the topic [[Marine biology in the instrumental period]]'' ...bal processes (Bargagli, 2005<ref name="Bargagli, 2005">Bargagli, R. 2005. Antarctic Ecosystems: Environmental Contamination, Climate Change, and Human Impact.38 KB (5,770 words) - 15:33, 6 August 2014
- :''This page is part of the topic [[Observations, data accuracy and tools]]'' ...atic stations. A further boost to the observing network has taken place in the International Polar Year of 2007 – 2008.59 KB (9,046 words) - 15:33, 6 August 2014
- :''This page is part of the topic [[The Southern Ocean in the instrumental period]]'' ...shortcomings, so their results have to be considered with as much care as the ones derived from observations alone. Indeed, some models throw up contradi8 KB (1,343 words) - 15:33, 6 August 2014
- :''This page is part of the topic [[Observations, data accuracy and tools]]'' ...es. In this section we examine some of the major classes of models used in Antarctic studies.2 KB (322 words) - 15:33, 6 August 2014
- :''This page is part of the topic [[Marine biology over the next 100 years]]'' ...rrigno, J. 2005, Retreating glacier fronts on the Antarctic Peninsula over the past half-century, ''Science'', '''308''', 541-544.</ref>).54 KB (8,443 words) - 17:49, 22 August 2014
- :''This page is part of the topic [[The Antarctic environment in the global system]]'' ...as meteorology, solar-terrestrial interactions in the Earth’s outer atmosphere (known as ‘geospace’), coastal sea ice conditions, and sea leve5 KB (752 words) - 15:09, 22 August 2014
- ...page is part of the topic [[Antarctic climate and environment change over the next 100 years]]'' ==Simulation of present-day conditions in the Southern Ocean.==33 KB (5,321 words) - 15:57, 22 August 2014
- ...rt of the topic [[Models of the physical and biological environment of the Antarctic]]'' ...ost and physical realism. This is especially true for ocean models because the computational cost is always high, and can be hundreds of times that of a c37 KB (5,859 words) - 15:33, 6 August 2014
- :''This page is part of the topic [[Atmospheric change over the next 100 years]]'' ...s is paramount for resolving the uncertainty surrounding the future of the Antarctic ice sheet.18 KB (2,723 words) - 15:33, 6 August 2014
- ...ake place among some of the remotest and harshest environments anywhere on the Earth’s surface. ...rnational Geophysical Year of 1957-58. Many more results also emerged from the [http://www.ipy.org/ International Polar Year] of 2007-2008.5 KB (766 words) - 17:45, 21 August 2014
- ...ailable with which to investigate change – both in the past and over the next century, there are still major gaps in our knowledge and many areas wh ...limate change on geological time scales. In addition, scattered throughout the text there are many statements about additional research requirements.14 KB (2,069 words) - 16:14, 22 August 2014
- ...rt of the topic [[Models of the physical and biological environment of the Antarctic]]'' ...n a subgrid scale – like the scale of the Antarctic Peninsula. While the spatial resolution of GCMs will increase, their capabilities will continue5 KB (833 words) - 15:33, 6 August 2014
- :''This page is part of the topic [[Observations, data accuracy and tools]]'' ...ography, and their utility is nowhere greater than in data-poor regions of the Southern Ocean. They include, for example: - altimeters, scatterometers, in20 KB (3,084 words) - 15:57, 6 August 2014
- ...rt of the topic [[Models of the physical and biological environment of the Antarctic]]'' ...lgal growth (Garrison, 1991<ref name="Garrison, 1991">Garrison, D.L. 1991. Antarctic sea ice biota, ''Am. Zool.'', '''31''', 17-33.</ref>).18 KB (2,786 words) - 15:33, 6 August 2014
- :''This page is part of the topic [[The last million years]]'' ...Pichon, J.J. 2004. Late Qaternary sea ice history in the Indian sector of the Southern Ocean as record by diatom assemblages, ''Marine Micropaleontology'13 KB (2,050 words) - 15:33, 6 August 2014
- :''This page is part of the topic [[The Southern Ocean in the instrumental period]]'' ...uantification of such processes is a prerequisite for successful modelling the large scale conditions.18 KB (2,816 words) - 15:33, 6 August 2014
- ...is page is part of the topic [[Antarctic climate and environment change in the instrumental period]]'' ...tic can be determined using a number of different forms of data, including the ''in-situ'' observations, satellite infra-red imagery and ice core isotope30 KB (4,676 words) - 18:04, 22 August 2014
- :''This page is part of the topic [[Atmospheric change over the next 100 years]]'' [[File:Figure 5.6 - Skin temperature trend over the Twenty First Century.png|thumb|'''5.6''' Skin temperature trend over Twenty8 KB (1,217 words) - 15:34, 6 August 2014
- :''This page is part of the topic [[The Southern Ocean in the instrumental period]]'' ...0300-005-0058-5.</ref>). A comprehensive field study on Antarctic krill in the Amundsen Sea has yet to be conducted.11 KB (1,650 words) - 15:34, 6 August 2014
- :''This page is part of the topic [[Biological responses to 21st climate climate change]]'' ...scale detail in predictions of change in the physical environment, e.g. of the likelihood and extent of extreme events, and of fine scale spatial resoluti20 KB (3,055 words) - 15:34, 6 August 2014
- :''This page is part of the topic [[The Southern Ocean in the instrumental period]]'' ...">Rintoul, S.R. 2007. Rapid freshening of Antarctic Bottom Water formed in the Indian and Pacific Oceans, ''Geophys. Res. Lett.'', '''34''', L06606, doi:114 KB (2,205 words) - 15:34, 6 August 2014
- :''This page is part of the topic [[The Antarctic environment in the global system]]'' ...(dark) ocean, solar radiation will be absorbed rather than reflected, and the environment will warm.12 KB (1,933 words) - 16:38, 22 August 2014
- :''This page is part of the topic [[Deep time]]'' ...ical Research'', '''99''', 15115-15139.</ref>). The shaded area represents the modelled error envelope.]]20 KB (3,076 words) - 15:34, 6 August 2014
- ...s page is part of the topic [[Antarctic climate and environment history in the pre-instrumental period]]'' ...ironmental change experienced in the major regions of Antarctica which are the result of both continental and local forcing mechanisms.1 KB (199 words) - 15:34, 6 August 2014
- ...is page is part of the topic [[Antarctic climate and environment change in the instrumental period]]'' ...rn of flow specific to the current climate, where flow exactly compensates the spatial pattern of ice accumulation (snowfall and frost deposition) and ice20 KB (3,052 words) - 16:00, 6 August 2014