Search results
Create the page "Antarctic sea ice" on this wiki! See also the search results found.
Page title matches
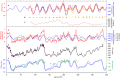
File:Figure 3.10 - Accurately dated Antarctic ice-core records and the comparison with sea level proxies.png ...sy, J.C., McManus, J.F., Lambeck, K., Balbon, E. and Labracherie, M. 2002. Sea level and deep water temperature changes derived from bentic foraminifera i(611 × 396 (118 KB)) - 15:30, 6 August 2014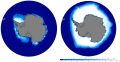
File:Figure 1.7 - Antarctic summer and winter sea ice extent.png Sea ice extent in summer (February 2008) at left, and in winter (September 2008) at(600 × 311 (84 KB)) - 15:31, 6 August 2014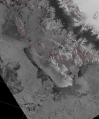
File:Figure 2.19 - Envisat ASAR image showing sea ice around Adelaide Island, West Antarctic Peninsula.png Envisat ASAR image showing sea ice around Adelaide Island, West Antarctic Peninsula(471 × 568 (353 KB)) - 15:31, 6 August 2014- :''This page is part of the topic [[Antarctic climate and environment change in the instrumental period]]'' ...1970s microwave instruments on polar orbiting satellites have enabled sea ice observations to be made year-round and even during periods of complete clou22 KB (3,536 words) - 13:25, 22 August 2014
Page text matches
File:Figure 4.4 - El Nino and La Nina SST anomaly composites and schematic effects.png ...impacts on Antarctic sea ice: a synthesis of phenomenon and mechanisms, ''Antarctic Science'', '''16'''(4), 415-425.</ref>).(549 × 688 (669 KB)) - 15:30, 6 August 2014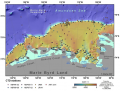
File:Figure 4.25 - Amundsen Sea bathymetric chart and hydrographic stations of different cruises.png ..., Jacobs, S.S., Larter, R.D. and Gohl, K. 2007. Bathymetry of the Amundsen Sea continental shelf: Implications for geology, oceanography, and glaciology,(637 × 481 (343 KB)) - 15:30, 6 August 2014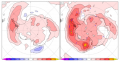
File:Figure 5.2 - Temperature trends for 1960-2000 for winter (JJA).png ...lley and Bracegirdle, 2007">Connolley, W.M. and Bracegirdle, T.J. 2007. An Antarctic assessment of IPCC AR4 coupled models, ''Geophys. Res. Lett.'', '''34''', L(554 × 288 (145 KB)) - 15:30, 6 August 2014
File:Figure 3.10 - Accurately dated Antarctic ice-core records and the comparison with sea level proxies.png ...sy, J.C., McManus, J.F., Lambeck, K., Balbon, E. and Labracherie, M. 2002. Sea level and deep water temperature changes derived from bentic foraminifera i(611 × 396 (118 KB)) - 15:30, 6 August 2014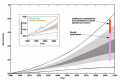
File:Figure 5.19 - Projected sea-level rise for the Twenty First Century.png ...tional contribution from a dynamic response of the Greenland and Antarctic ice sheets to global warming. The inset shows the 2001 projection compared with(532 × 353 (134 KB)) - 15:31, 6 August 2014
File:Figure 3.20 - Signals of climate change in ice core records from Siple Dome and Law Dome.png ...in atmospheric CO2 over the last 1000 years from air in Antarctic firn and ice, ''J. Geophys. Res.'', '''101''', 4115-4128.</ref>). Darkened area shows th(436 × 702 (289 KB)) - 15:31, 6 August 2014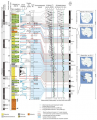
File:Figure 3.8 - Lithological column for the upper 600m of the AND-1B drillcore.png ..., Wilch, T. and Williams, T. 2009. Obliquity-paced Pliocene West Antarctic ice sheet oscillations, ''Nature'', '''458''', 322-328.</ref>).(562 × 694 (486 KB)) - 15:31, 6 August 2014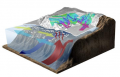
File:Figure 4.41 - Pictorial view of the ocean-ice system of the Ross Sea.png ...ere (wavy vertical line) while the remainder circulated under the floating ice shelf causing basal melting. (illustration courtesy of National Geographic)(533 × 342 (194 KB)) - 15:31, 6 August 2014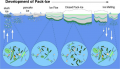
File:Figure 2.38 - Schematic of incorporation of biological material into Antarctic pack ice.png ...em, A.L. 2002. Modeling physical and biological processes in Antarctic sea ice. Ph.D. thesis, Alfred Wegener Institute for Polar and Marine Research, Brem(553 × 317 (207 KB)) - 15:31, 6 August 2014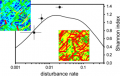
File:Figure 5.31 - Benthic diversity on the Antarctic shelf predicted for a range of disturbance rates.png ...., Johst, K. and Gutt, J. 2006. How to survive as a pioneer species in the Antarctic benthos: minimum dispersal distance as a function of lifetime and disturban(337 × 213 (53 KB)) - 15:31, 6 August 2014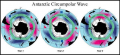
File:Figure 4.5 - Schematic summary of interannual variations in SST, sea level pressure and sea ice extent.png ...Antarctic Circumpolar Wave in surface pressure, wind, temperature, and sea ice extent, ''Nature'', '''380''', 699-702.</ref>).(554 × 254 (220 KB)) - 15:31, 6 August 2014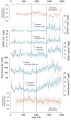
File:Figure 3.21 - Reconstructed temperatures and ice core reconstructed atmospheric circulation systems.png ...ere chosen because they are the highest resolution Antarctic and Greenland ice core data of their kind available. Figure taken from Mayewski and Maasch (2(398 × 675 (293 KB)) - 15:31, 6 August 2014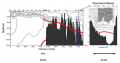
File:Figure 4.26 - Cross-section showing warm water penetrating the Pine Island Bay sub-ice shelf cavity.png .... Res. Ser.'', '''75''', 83-99.</ref>). The solid black area indicates the sea bed.(592 × 309 (119 KB)) - 15:31, 6 August 2014
File:Figure 2.33 - Bed elevations of the Amundsen Sea Embayment.png ...below sea level, with deeper blue signifying greater depths. The Amundsen Sea is in the lower left corner. Comparison shows that the recent surveys provi(447 × 250 (342 KB)) - 15:31, 6 August 2014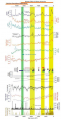
File:Figure 3.19a - Antarctic and Greenland holocene climate change compared using ice core data.png ...n, E.D. 1999. Past and future grounding-line retreat of the West Antarctic Ice Sheet. Science 286:280-283.</ref>). Figure modified from Mayewski et al. (2(414 × 807 (400 KB)) - 15:31, 6 August 2014
File:Figure 2.19 - Envisat ASAR image showing sea ice around Adelaide Island, West Antarctic Peninsula.png Envisat ASAR image showing sea ice around Adelaide Island, West Antarctic Peninsula(471 × 568 (353 KB)) - 15:31, 6 August 2014
File:Figure 3.14 - Climate and environmental records of Termination I.png ...i, B.S., Tison, J.L., Werner, M. and Wolff, E. 2007. Orbital and millenial Antarctic climate variability over the past 800,000 years, ''Science'', '''317''', 79(418 × 649 (125 KB)) - 15:31, 6 August 2014
File:Figure 3.17 - Sea ice distribution at the Southern Ocean EPILOG-LGM time slice.png ...ribution of the Southern Ocean at the EPILOG Last Glacial Maximum-a circum-Antarctic view based on siliceous microfossil records, ''Quaternary Science Reviews''(552 × 520 (145 KB)) - 15:31, 6 August 2014
File:Figure 3.7 - View of the Victoria Land coast off Cape Roberts during Oligocene and early Miocene times.png ...white filled circle. TAM = Transantarctic Mountains, EAIS = East Antarctic Ice Sheet.(479 × 471 (169 KB)) - 15:31, 6 August 2014- :''This page is part of the topic [[Antarctic climate and environment change over the next 100 years]]'' ...lly by melting of land-based sources of ice (glaciers and ice caps and the ice sheets of Greenland and Antarctica). The amount of thermal expansion is non16 KB (2,491 words) - 13:16, 22 August 2014
- ...orological conditions across the Southern Ocean, ocean conditions, the sea ice extent and the terrestrial and marine biology. ...this really began the period of organised scientific investigation in the Antarctic. Most of these stations were not operated for long periods, which is a hand3 KB (501 words) - 16:48, 6 August 2014
- ...t for both scientists and policymakers concerned with issues as diverse as sea-level rise and fish stocks. A major problem is that we still have a poor un ...ojections for temperature and precipitation were used to estimate how much sea level would rise under various greenhouse gas emission scenarios. In the fo5 KB (788 words) - 16:49, 6 August 2014
- ...and its effects on global sea level, and the changing distribution of sea ice and its effect on climate are then described. ...nt interglacial, the Holocene is described in detail from a combination of ice cores, marine sediments, lake sediments and terrestrial records with a focu17 KB (2,554 words) - 16:45, 6 August 2014
- ...as changed from Deep Time until the present day. It also considers how the Antarctic environment may change over the next century in a world where greenhouse ga ...fic Committee on Antarctic Research ([http://www.scar.org/ SCAR]) known as Antarctic Climate Change and the Environment (ACCE), which is described in [[About AC4 KB (504 words) - 17:51, 21 August 2014
- ...at the LGM from ice-dynamic reconstructions of the Greenland and Antarctic ice sheets during the glacial cycles, ''Quaternary Science Reviews'', '''21''', ...ce the eustatic contribution and so there is a continuous fall in relative sea level like that seen in areas such as Hudson Bay or Sweden today.21 KB (3,294 words) - 15:33, 6 August 2014
- :''This page is part of the topic [[Antarctic climate and environment change in the instrumental period]]'' ...1970s microwave instruments on polar orbiting satellites have enabled sea ice observations to be made year-round and even during periods of complete clou22 KB (3,536 words) - 13:25, 22 August 2014
- ==Antarctic stratospheric ozone over the next 100 years== ...averaged over some period, and it is the most accurate diagnostic of total Antarctic ozone loss.</li>27 KB (4,305 words) - 16:22, 6 August 2014
- :''This page is part of the topic [[Antarctic climate and environment change in the instrumental period]]'' ==Antarctic stratospheric ozone in the instrumental period==43 KB (6,788 words) - 17:07, 22 August 2014
- :''This page is part of the topic [[Antarctic climate and environment change in the instrumental period]]'' ...08. Here the SAM is in its positive phase with negative anomalies over the Antarctic and positive anomalies over the Southern Ocean.]]54 KB (8,177 words) - 13:38, 22 August 2014
- ...ulation in the warming of the Antarctic Peninsula, the distribution of sea ice, and the seasonal to interannual variability of the Southern Hemisphere. ...y, analyses of sea level pressure have revealed secular decreases over the Antarctic, associated with increases in mid-latitude westerlies, a poleward displacem29 KB (4,462 words) - 17:11, 22 August 2014
- :''This page is part of the topic [[The ice sheet in the instrumental period]]'' ...such as recent/anthropogenic climate change. The inescapable fact is that ice sheet behaviour manifests itself as the superposition of multiple responses13 KB (1,943 words) - 15:33, 6 August 2014
- ...rt of the topic [[Models of the physical and biological environment of the Antarctic]]'' ...y production, and are either supported or reduced by the occurrence of sea ice (Beaman and Harris, 2005<ref name="Beaman and Harris, 2005">Beaman, R.J. an8 KB (1,225 words) - 15:33, 6 August 2014
- ...sonality of high latitudes, phenology is a key aspect of the adaptation of Antarctic organisms and populations to change, and can be used to evaluate the match ...., Baroni, C., Lambert, D.M. 2005. Microevolution and mega-icebergs in the Antarctic, ''Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci.'', '''102''', 16717-16722</ref>). This suggests t16 KB (2,488 words) - 15:33, 6 August 2014
- :''This page is part of the topic [[Antarctic climate and environment change in the instrumental period]]'' ==General spatial and temporal characteristics of Antarctic snowfall==20 KB (3,125 words) - 15:33, 6 August 2014
- ...e it will be essential to use proxy records to represent how Antarctic sea ice has changed in the past. ...ichon, J.J. and Burckle, L.H. 1998b. Reappraisal of Antarctic seasonal sea-ice at the Last Glacial Maximum, ''Geophysical Research Letters'', '''25''', 2724 KB (3,785 words) - 17:17, 22 August 2014
- :''This page is part of the topic [[Antarctic climate and environment change over the next 100 years]]'' ...xy data and analogues exist. The broad range of time scale response of the ice sheet guarantees that future behaviour will be composed of a superposition26 KB (4,124 words) - 14:04, 22 August 2014
- :''This page is part of the topic [[Antarctic climate and environment history in the pre-instrumental period]]'' ...ter resolution both temporally (for instance, in the phasing of changes in Antarctic climate, environmental parameters and atmospheric composition) and spatiall7 KB (1,082 words) - 15:33, 6 August 2014
- :''This page is part of the topic [[The ice sheet in the instrumental period]]'' ...e been considered unlikely even a decade ago. The geographic extent of the ice sheet places different parts in markedly different positions within the glo3 KB (475 words) - 15:33, 6 August 2014
- ...rt of the topic [[Models of the physical and biological environment of the Antarctic]]'' ...r strengths and weaknesses, before presenting some results relevant to the Antarctic from the models used in the IPCC AR4.13 KB (2,051 words) - 15:33, 6 August 2014
- ...nsula Climate Variability: Historical and Paleoenvironmental Perspectives, Antarctic Research Series, 79. American Geophysical Union.</ref>). ...bsequently, numerous studies have addressed the questions of how large the ice sheets were during the LGM, and when they began their retreat.22 KB (3,430 words) - 13:03, 22 August 2014
- ...the Global Climate System from 2005 to 2008. He is the co-author of ‘Antarctic Meteorology and Climatology’ and ‘Polar Lows: Mesoscale Weather ...n quoted commenting on glaciological impacts of the climate on the world's ice sheets and glaciers.7 KB (1,089 words) - 15:33, 6 August 2014
- ...summer mean krill density correleated positively with the duration of sea ice the previous winter (Atkinson et al., 2004<ref name="Atkinson et al, 2004"> ...res probably reflect a distribution and dispersal effect across the Scotia Sea and the degree of influence of cooler polar waters in northern regions arou15 KB (2,381 words) - 15:33, 6 August 2014
- ...ignificant problem for researchers in many areas of Antarctic science. The Antarctic continent is large and there are logistical difficulties in getting to many ...launch in coming years, many of which will directly benefit studies of the Antarctic. While not exhaustive because of changing plans, some of these are briefly7 KB (1,040 words) - 16:16, 22 August 2014
- ...ng|thumb|'''3.9''' Main climatic events of the last 1 Million years in the Antarctic context]] ...sy, J.C., McManus, J.F., Lambeck, K., Balbon, E. and Labracherie, M. 2002. Sea level and deep water temperature changes derived from bentic foraminifera i35 KB (5,415 words) - 15:33, 6 August 2014
- ...the lakes, likely related to increased nutrient inputs and a reduction in ice and snow cover at c. 10.2 ka BP, marking the start of relatively warm condi ...Evolution and Processes. Proceedings of the VII International Symposium on Antarctic Earth Sciences, Siena, 1995. Terra Antarctica, Sienna, 809-820.</ref>).38 KB (5,787 words) - 17:39, 22 August 2014
- ...nsula.png|thumb|'''3.26''' Selected Holocene environmental changes – Antarctic Peninsula]] ...story of the Antarctic Peninsula since the Last Glacial Maximum, Arctic, ''Antarctic and Alpine Research'', '''35''', 175-186.</ref>).32 KB (5,127 words) - 17:41, 22 August 2014
- ....png|thumb|'''3.28''' Selected Holocene environmental changes – Ross Sea]] ...e Wright, a high-level Antarctic lake during the LGM and early Holocene, ''Antarctic Science'', '''13''', 53-60.</ref>). The large amount of water in these lake17 KB (2,705 words) - 17:43, 22 August 2014
- ...een sufficient variability during the last ~9 ka to cause major changes to Antarctic ecosystems. This natural variability must be taken into account in understa ...n, E.D. 1999. Past and future grounding-line retreat of the West Antarctic Ice Sheet. Science 286:280-283.</ref>). Figure modified from Mayewski et al. (239 KB (5,945 words) - 15:33, 6 August 2014
- ...rt of the topic [[Models of the physical and biological environment of the Antarctic]]'' ...lication of a continuum-mechanical model for the flow of anisotropic polar ice to the EDML core, Antarctica.33 KB (5,053 words) - 15:33, 6 August 2014
- ...ns in the Ocean-Ocean Processes and Marine Population Dynamics. California Sea Grant College System, La Jolla.</ref>; Finney et al., 2002<ref name="Finney ...thermal specialization paradigm: compensation for elevated temperatures in Antarctic fish, ''Biol. Lett.'', '''2''', 151-154.</ref>).25 KB (3,817 words) - 15:33, 6 August 2014