File:Figure 3.20 - Signals of climate change in ice core records from Siple Dome and Law Dome.png
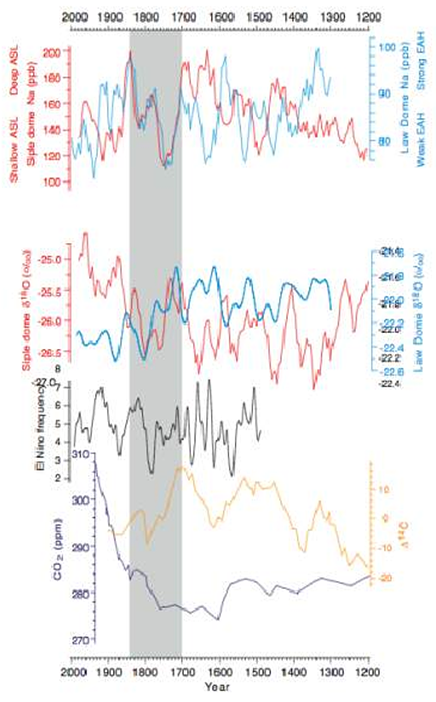
25 year running mean of SD (Siple Dome (red)) and DSS (Law Dome (blue) Na+ (ppb) used as a proxy for the ASL (Amundsen Sea Low) and EAH (East Antarctic High), respectively, with estimated sea level pressure developed from calibration with the instrumental and NCEP reanalysis (based on Kreutz et al., 2000; Souney et al., 2002[1]). Twenty five year running mean SD (red) and DSS (blue) 18O (o/oo) used as a proxy for temperature, with estimated temperature developed from calibration with instrumental mean annual and seasonal temperature values (van Ommen and Morgan, 1996[2]; Steig et al., 2000[3]). Frequency of El Niño polar penetration (black) based on calibration between the historical El Niño frequency record (Quinn et al., 1987[4]; Quinn and Neal, 1992[5]) and SP MS (methanesulfonate) (Meyerson et al., 2002[6]). Figure from Mayewski et al. (2005). δ14C series used as an approximation for solar variability (Stuiver and Braziunas, 1993[7]). CO2 from DSS ice core (Etheridge et al., 1996[8]). Darkened area shows the 1700-1850 AD era climate anomaly discussed in the text.
- ↑ Souney, J., Mayewski, P.A., Goodwin, I., Morgan, V. and Van Ommen, T. 2002. A 700-year record of atmospheric circulation developed from the Law Dome ice core, East Antarctica, J. Geophys. Res., 107 (D22), 4608-4616.
- ↑ Van Ommen, T.D. and Morgan, V.I. 1996. Peroxide concentrations in the Dome Summit South ice core, Law Dome, Antarctica, J. Geophys. Res., 101 (D10) 15,147-15,152.
- ↑ Steig, E.J., Morse, D.L., Waddington, E.D., Stuiver, M., Grootes, P.M., Mayewski, P.A., Twickler, M.S. and Whitlow, S.I. 2000. Wisconsinan and Holocene climate history from an ice core at Taylor Dome, western Ross Embayment, Antarctica, Geografiska Annaler Series a-Physical Geography, 82A, 213-235.
- ↑ Quinn, W.H., Neal, V.T. and Antunez De Mayolo, S.E. 1987. El Nino occurrences over the past four and a half centuries, J. Geophys. Res., 92, C13, 14449-14461.
- ↑ Quinn, W.H. and Neal, V.T. 1992. The historical record of El Nino events, In Climate Since A.D. 1500, Eds. R.S. Bradley and P.D. Jones, Routledge, London, 623-648.
- ↑ Meyerson, E.A., Mayewski, P.A., Whitlow, S.I., Meeker, L.D., Kreutz, K.J. and Twickler, M.S. 2002. The extratropical expression of ENSO recorded in a South Pole glaciochemical time series, Annals of Glaciology, 35, 430-436.
- ↑ Stuiver, M. and Braziunas, T.F. 1993. Sun, ocean, climate, and atmospheric CO2: an evaluation of causal and spectral relationships, Holocene, 3(4), 289-305.
- ↑ Etheridge, D.M., Steele, L.P., Langenfields, R.J. Francey, J.M. Barnola and Morgan, V.I. 1996. Natural and anthropogenic changes in atmospheric CO2 over the last 1000 years from air in Antarctic firn and ice, J. Geophys. Res., 101, 4115-4128.
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 15:31, 6 August 2014 |  | 436 × 702 (289 KB) | Maintenance script (Talk) | Uploaded by import script |
- You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following page links to this file: